How to Submit Your Website to Search Engines
But here’s the thing: it takes time for search engines to discover (and index) new websites.
That means if you search for your two‐day‐old website in Google, chances are you’ll be disappointed. In fact, 9 times out of 10, you’ll find nothing.
However, even a few weeks after going live, you may still not see your website in Google, Bing and Yahoo, which have a combined market share of ~96%.
If this applies to you, and you now want to know the fastest way to submit your website to the search engines, then you’re in the right place. Here’s what we’ll be discussing in this article:
But first, let’s tackle the big question many people have in 2018…
Do you really need to submit your website to search engines?
Google and other search engines weren’t built to rely on manual submissions; that’s why they crawl the web.
Not familiar with crawling? It’s when search engines look for new links on websites and subsequently “follow” them. If a newly‐discovered link leads to something useful, that page is then added to the index.
Matt Cutts explains more about crawling and how it works in this video.
It’s also theorized that Google looks to many other data sources, such as Chrome browser usage statistics and domain registration data to aid in their never‐ending pursuit of new websites and webpages.
To summarise, this means that search engines are pretty good at discovering new websites and webpages on their own, provided that they’re linked‐to from somewhere on the web. (We’ll talk more about the importance of links later!)
Why you should still submit your website to search engines
Here are just a few reasons why manual submissions are still a “thing”:
- It’s better to be safe than sorry. Let’s face it, search engines will probably be able to find your website regardless of whether or not you choose to manually submit it. But is “probably” good enough? I mean, submitting your website only takes a minute‐or‐two. So why risk it?;
- Search engines can’t figure out everything via crawling. If you submit your website via the methods discussed below, you’ll have the opportunity to supply Google and Bing with some useful information about your website. For example, you can tell them how important you deem each of your pages to be. They couldn’t obtain this information from crawling alone.
- It helps to improve your website. Google and Bing each offer some insights as to how they view your website in their respective “management dashboards” (more on this later!). There are also various tools for testing your web pages, and they’ll alert you if and when potential problems or errors occur on your site.
Having said that, be aware that submitting your website to, and getting indexed by Google is only part of the battle. The real difficulty often lies in ranking for your desired search terms.
Don’t worry though, we’ve included some advice on how to do that in this very article.
But let’s not get ahead of ourselves.
How to submit your website to Google
It’s very easy to submit websites to Google (and other search engines).
Just watch our quick video tutorial or follow the written steps below.
Google discontinued their URLsubmission tool in July 2018. Now, the only way to submit your website is by adding your sitemap in Search Console.
What is a sitemap? It’s a file that lists all the pages on a website. It’s most commonly an XML file and looks something like this:
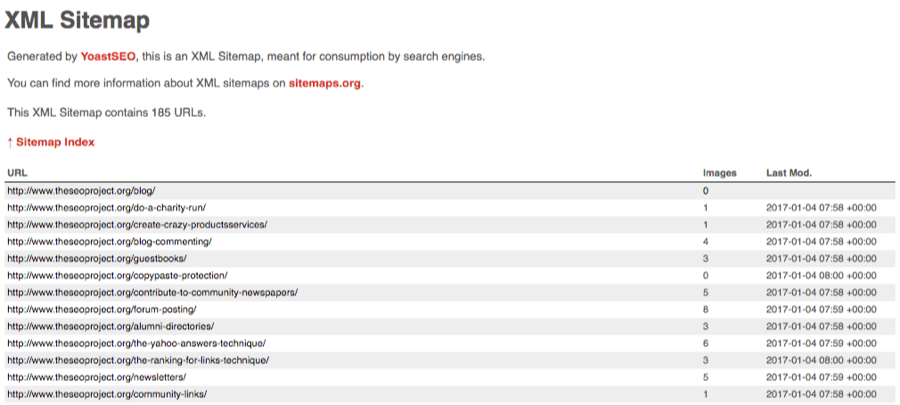
This particular sitemap lists all the blog posts on my personal blog.
Your sitemap is usually located at yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml. If you don’t see it there, check your robots.txt file by visiting yourdomain.com/robots.txt; this will usually list the sitemap URL.
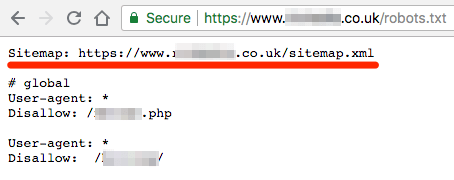
an example of the sitemap URL listed in a robots.txt file
You need to create one.
There are a few ways to do this. If you’re using WordPress (or another CMS), you can use one of many plugins for generating sitemaps automatically. We recommend Yoast SEO. For static websites, this sitemap generator works well. If you prefer a more manual/customized approach, follow this guide by Screaming Frog.
Found your sitemap? Good. You now need to submit it via Search Console.
Search Console > select your property > Sitemaps > paste in your sitemap URL > hit “submit”
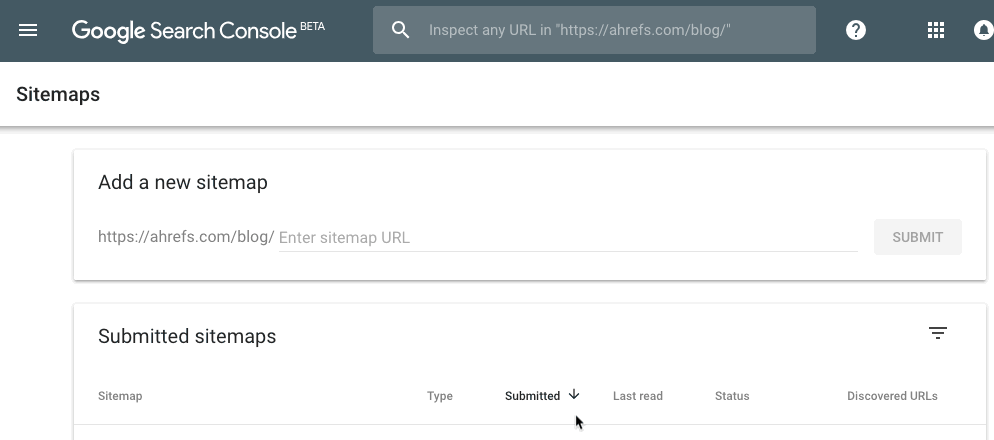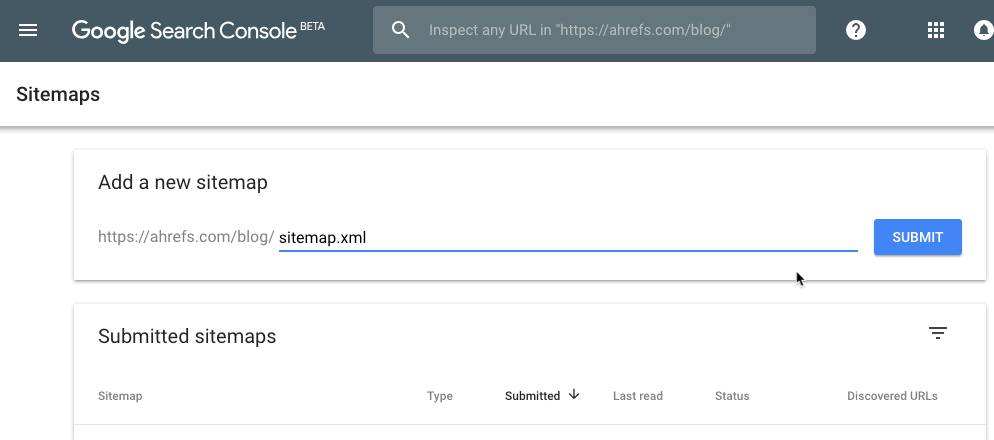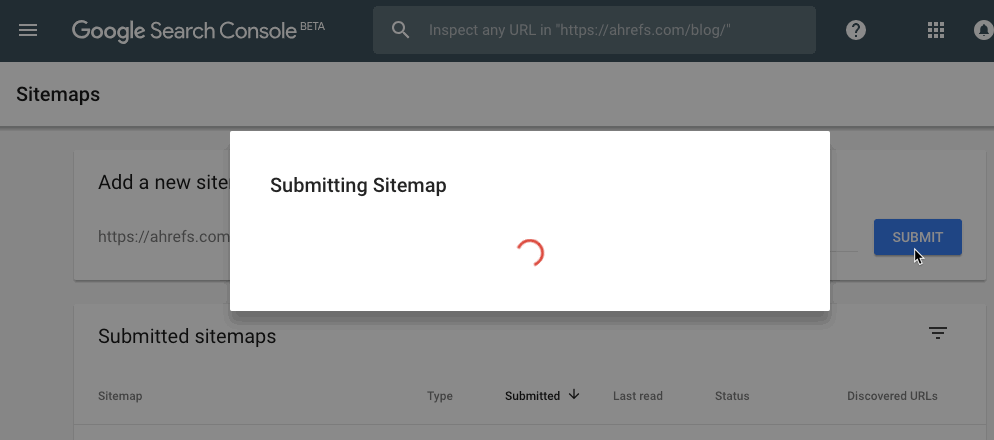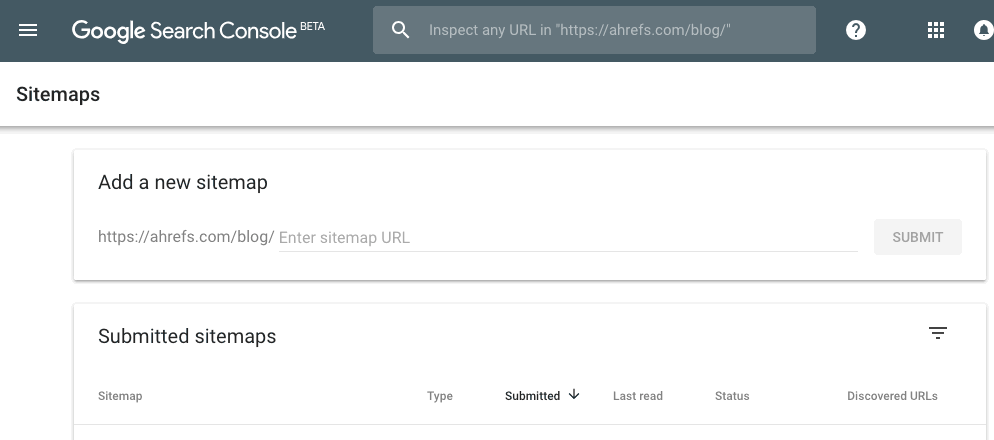
Note that I’m using the new beta version of Search Console. Here’s how to do it in the old one:
Search Console > select your property > Crawl > Sitemaps > Add/test sitemap > paste in your sitemap URL > hit “submit”
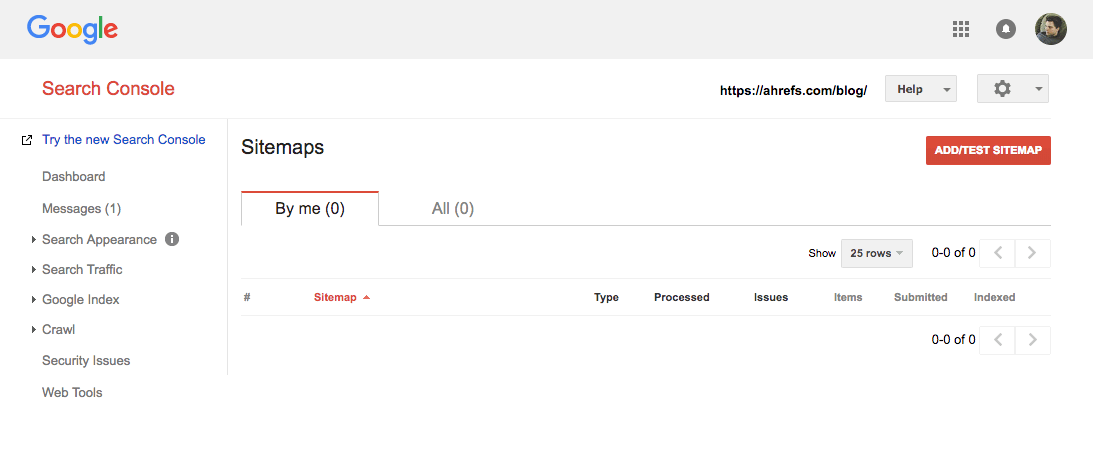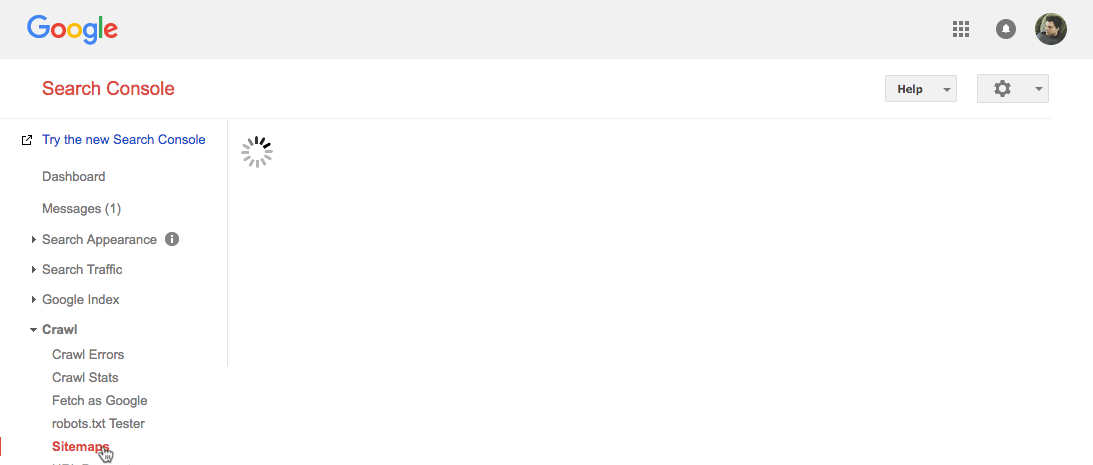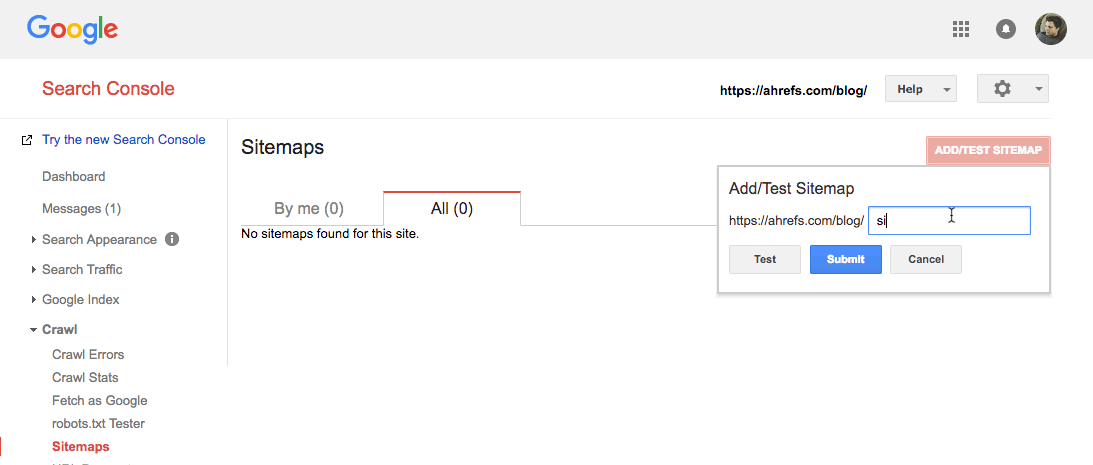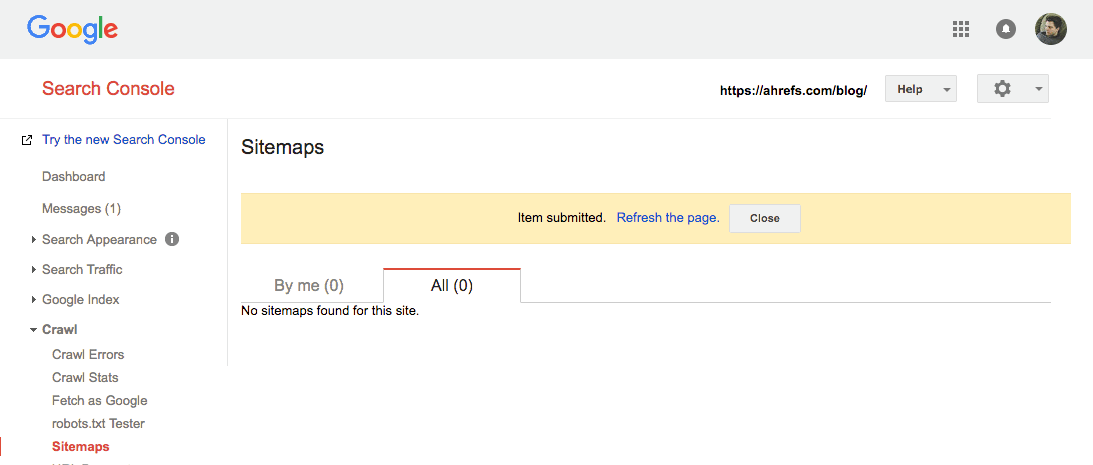
For those with multiple sitemaps (this may be the case when using a plugin like Yoast, or if you have a large site), just rinse and repeat this process.
What if I just want to submit an individual webpage to Google?
Google previously provided a way to do this via their URL submission tool, which was discontinued in 2018.
However, if you’re still using the old version of Search Console, you can submit individual URLs using the “Fetch as Google” tool. To do that, go to:
Search Console > Crawl > Fetch as Google > paste in your URL > Fetch
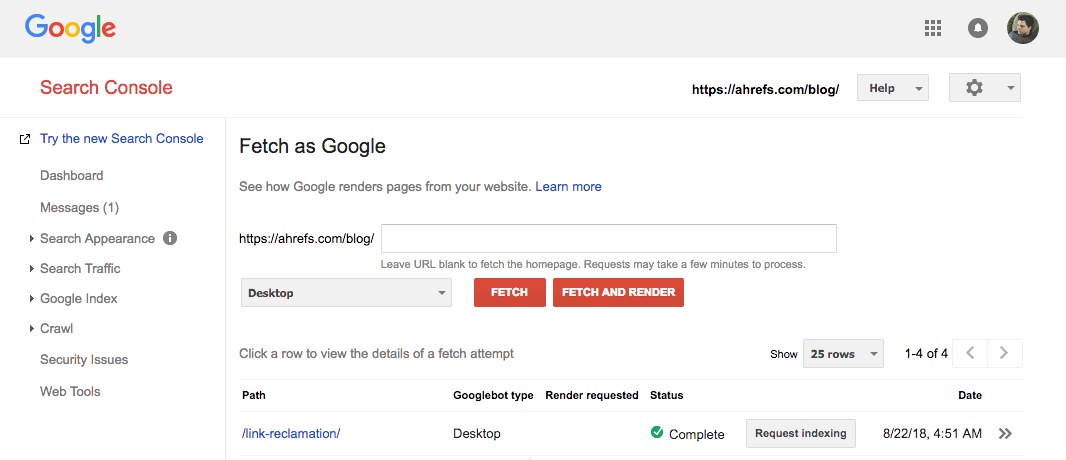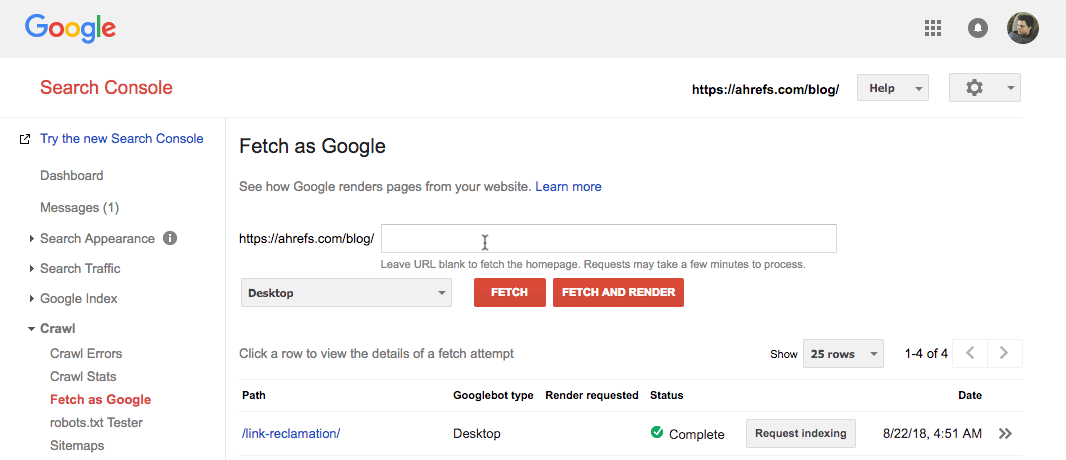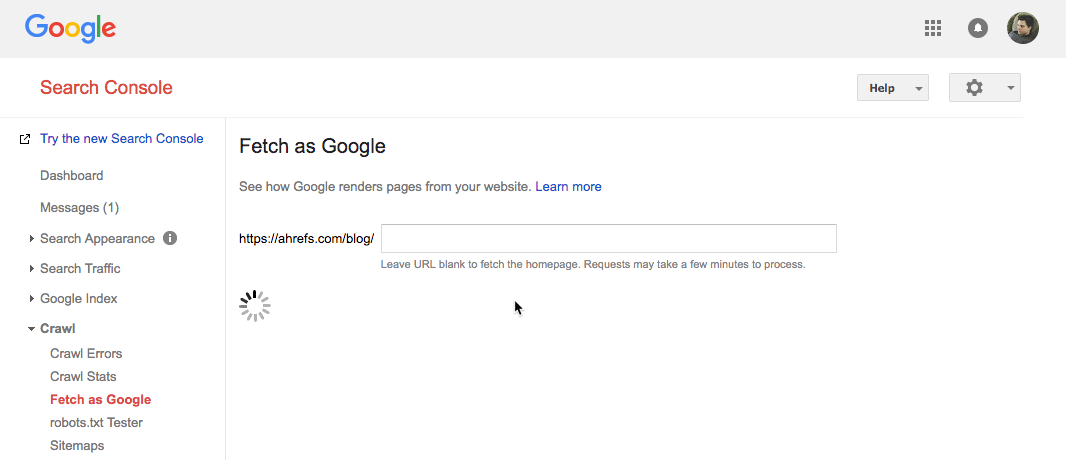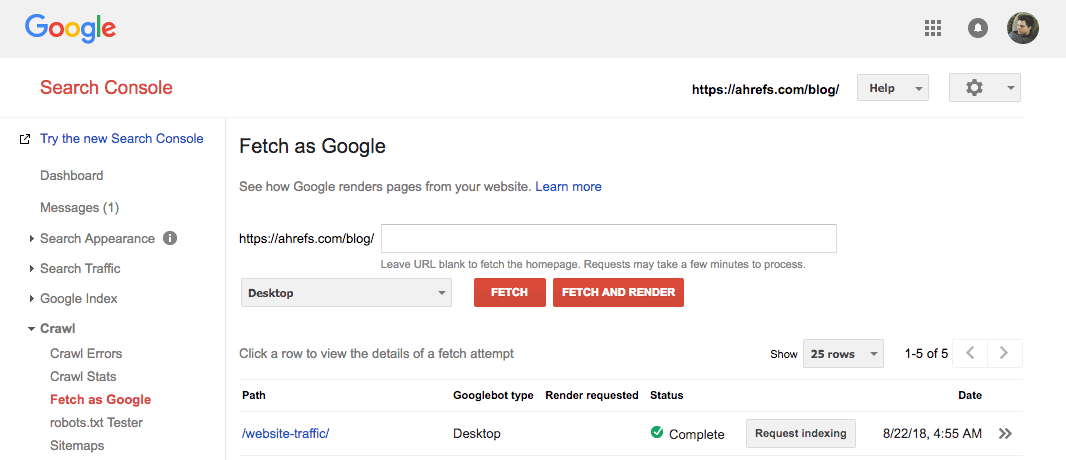
Next, you need to hit the “Request indexing” button, which brings up a modal box like this:
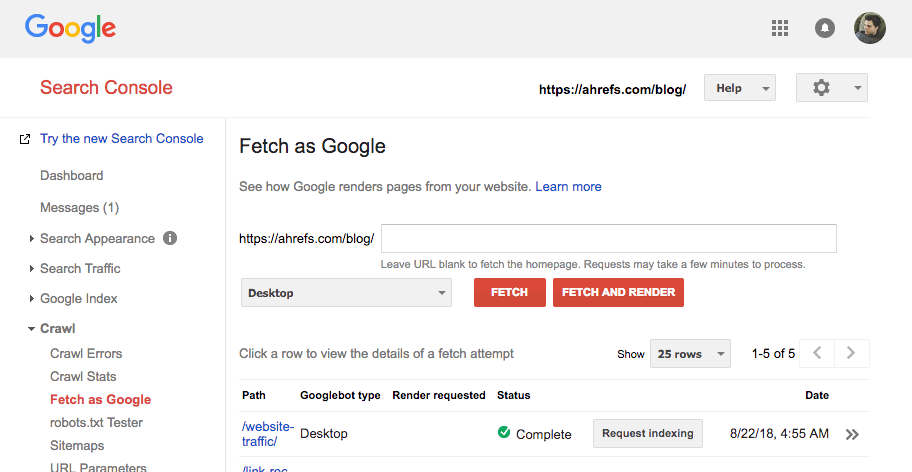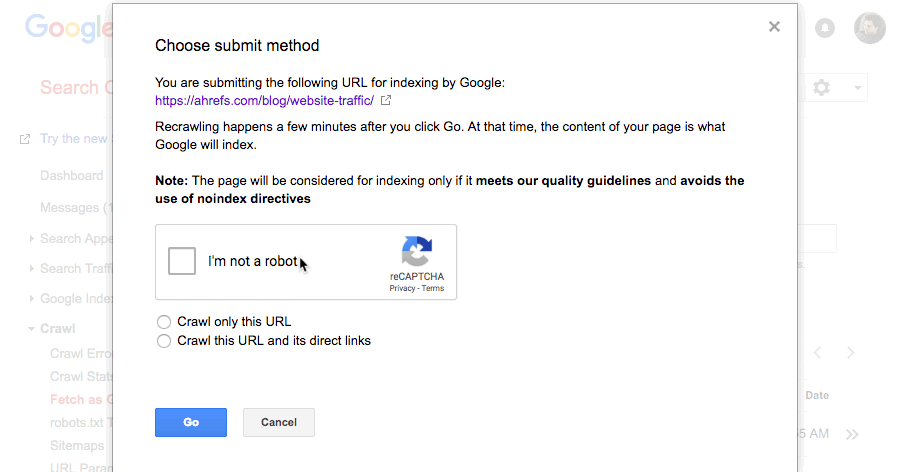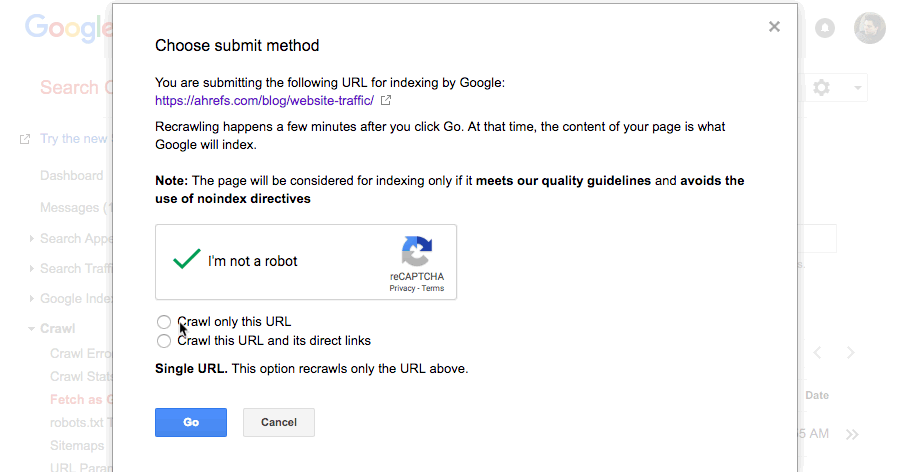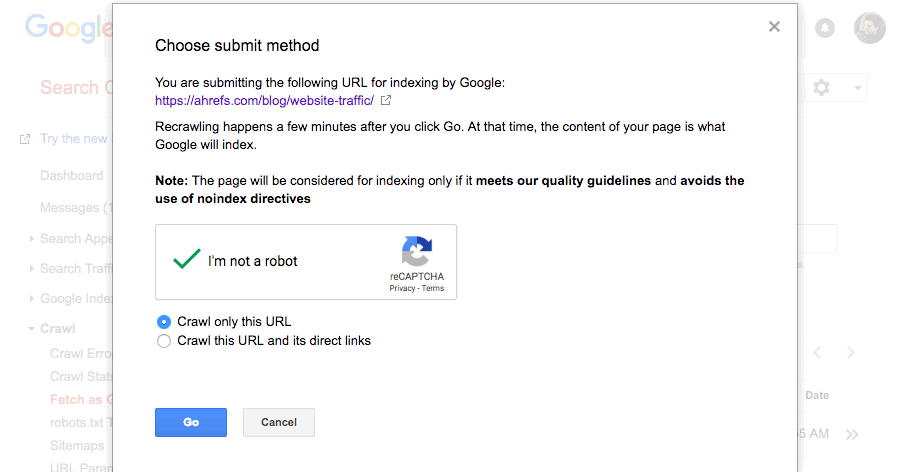
Tick that you’re not a robot (you’re not, are you!?), then choose whether you want Google to crawl just this URL, or this URL and its direct links.
That’s it. Job done.
But what about in the new Search Console? Can you still do this?
Well, it seems that Google has removed the “Fetch as Google” tool and replaced it with the URL inspection tool. The main purpose of this tool is to inspect URLs to uncover issues, but it may also work the same way as the old “Fetch as Google” tool when it comes to (re)crawling.
The problem is that Google’s instructions on the use of this tool don’t make much sense.
To submit a URL to the index:
1. Inspect the URL using the URLInspection tool.
2. Select Request indexing. The tool will run a live test on the URL to see whether it has any obvious indexing issues, and if not, the page will be queued for indexing. If the tool finds issues with the page you should try to fix them.
Inspecting the URL is easy enough; there’s just no “request indexing” button.
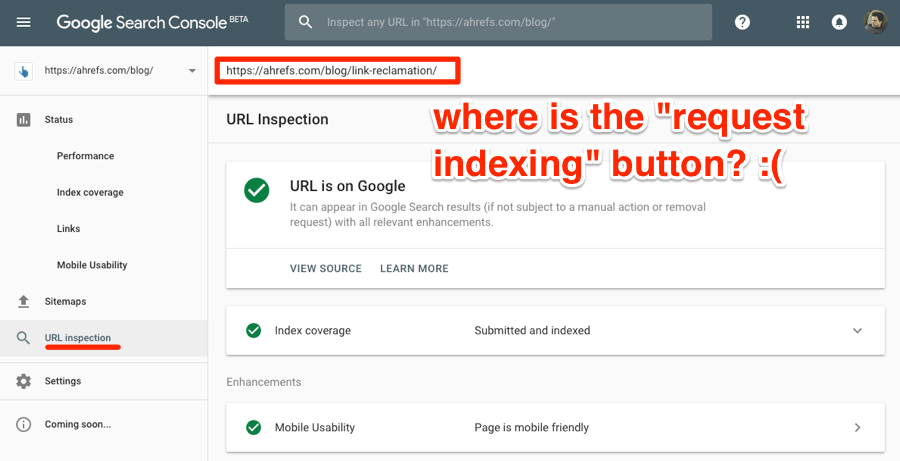
So, right now, we’re not sure how this works. However, this tool is still in beta, so chances are that Google will add this button at a later date.
For now, however, you should probably just stick to the “Fetch as Google” tool in the old version of Search Console.
How to submit your website to Bing and Yahoo
Unlike Google, Bing still has a public URL submission tool.
You can use this to submit any website (it doesn’t have to your own) to Bing in a matter of seconds. Just paste in homepage URL, fill in the captcha and hit submit.
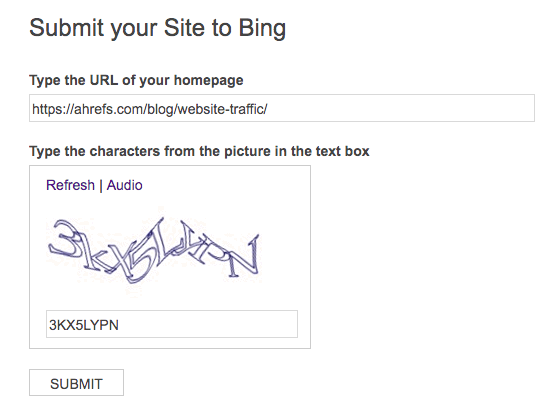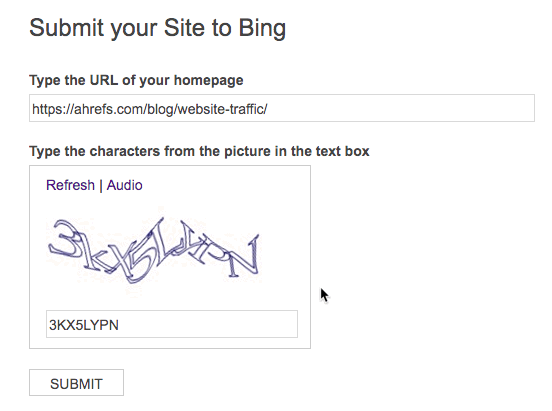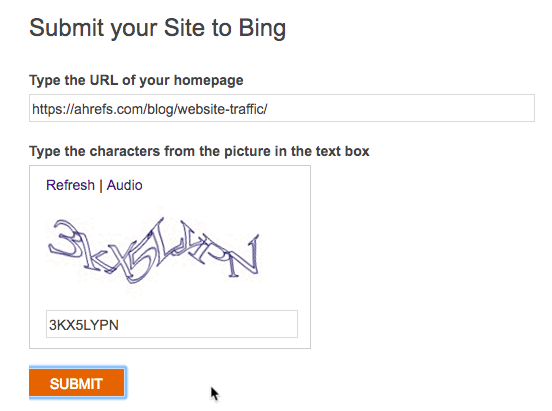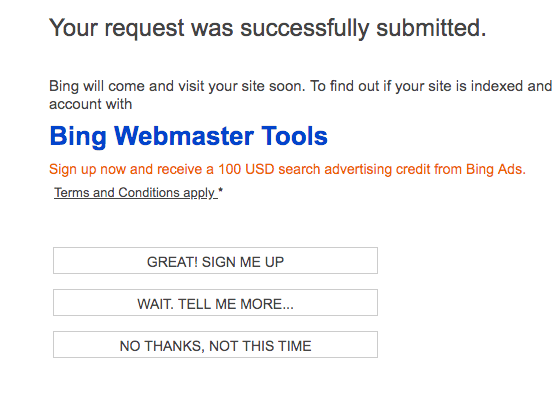
But this isn’t the method we’d recommend. It makes much more sense to submit your full sitemap within Bing Webmaster Tools.
Webmaster Tools > “add your site” > fill in the form > hit “submit”
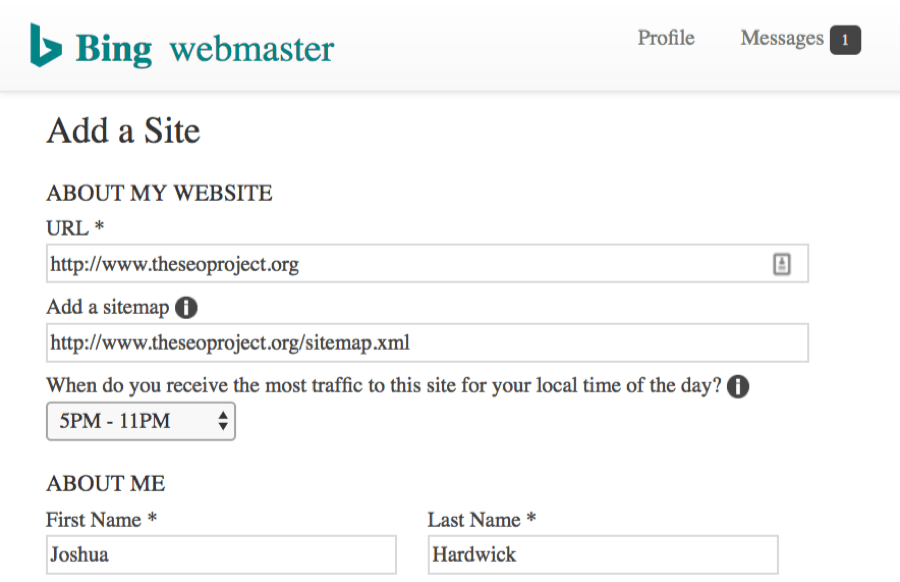
To submit your site to Yahoo, you don’t need to do anything. Yahoo is powered by Bing’s index. By submitting to Bing, your site will automatically be submitted to Yahoo.
How to check if your website is indexed
Using a “site” search in Google is the quickest way to check whether a site or webpage is indexed.
Here’s the syntax: site:yourdomain.com/page-to-check/
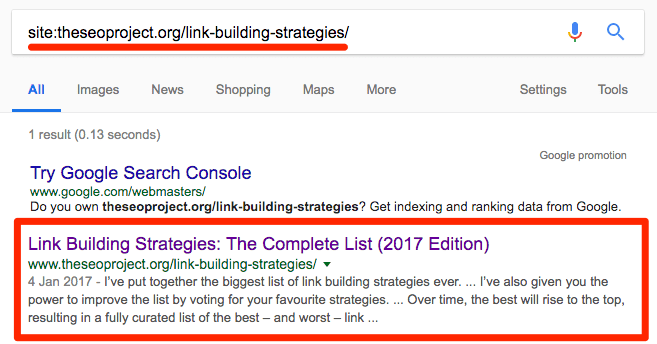
Using the “site” operator to check whether or not my list of link building strategies has been indexed in Google.
You can also check the index status of your site as a whole by using the site:operator combined with your domain, rather than a specific webpage.
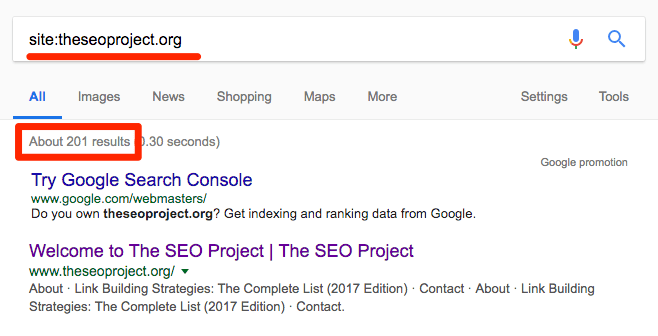
No results? Your website or webpage probably hasn’t been indexed.
Don’t worry if this remains the case for the first few days after publishing. If it still hasn’t been indexed after a week‐or‐two, however, there may be an issue.
You can also check the index status of your site in Google Search Console. However, only the new Google Search Console will show you a list of indexed pages.
Search Console > Status > Index Coverage
Go to the the “Valid” tab and select either “Indexed, not submitted in sitemap” or “Submitted and indexed” to see a list of pages in Google’s index.
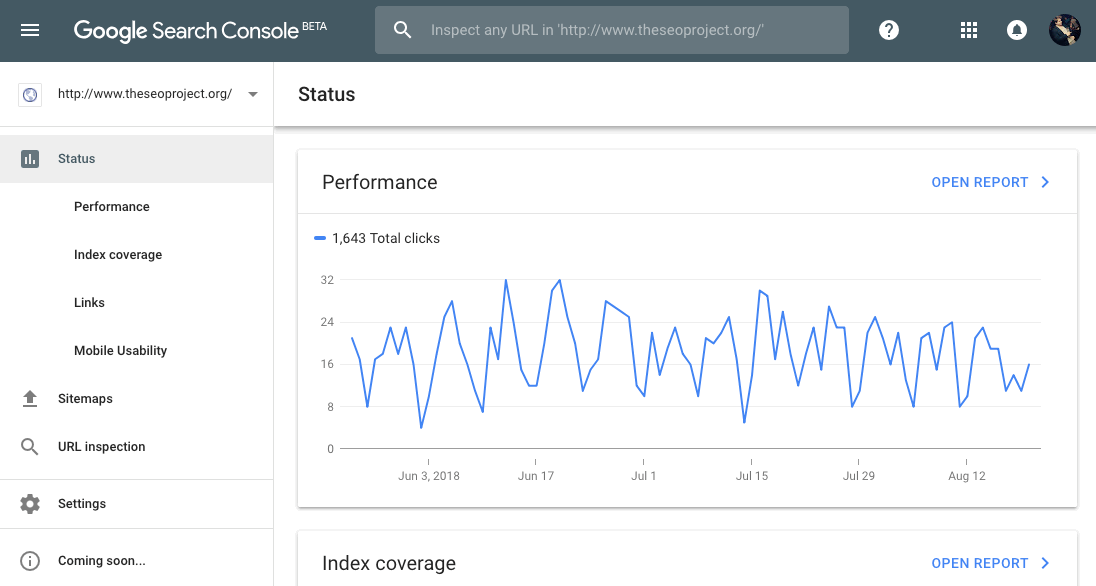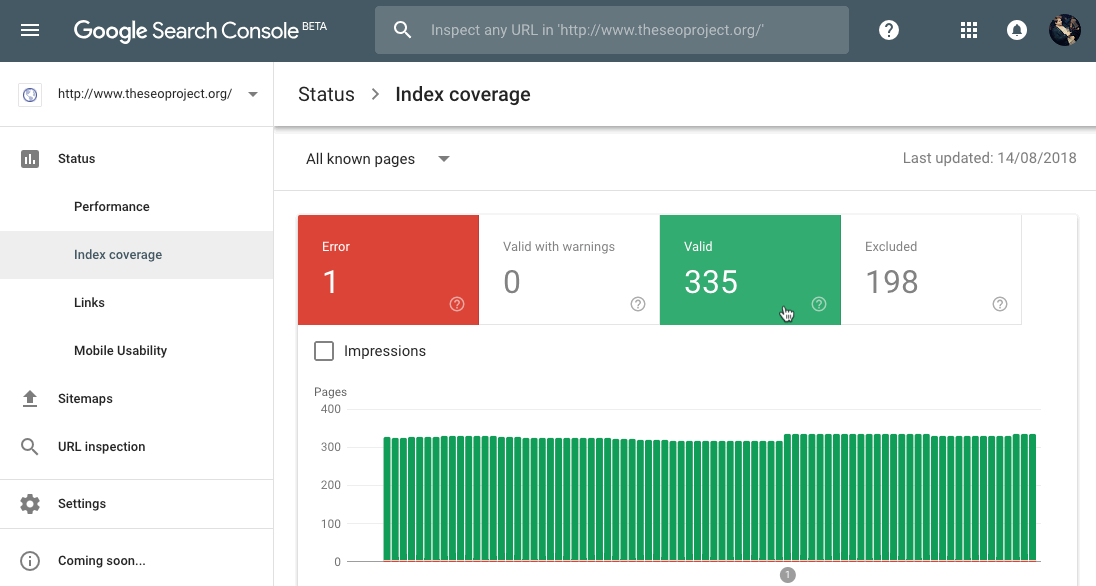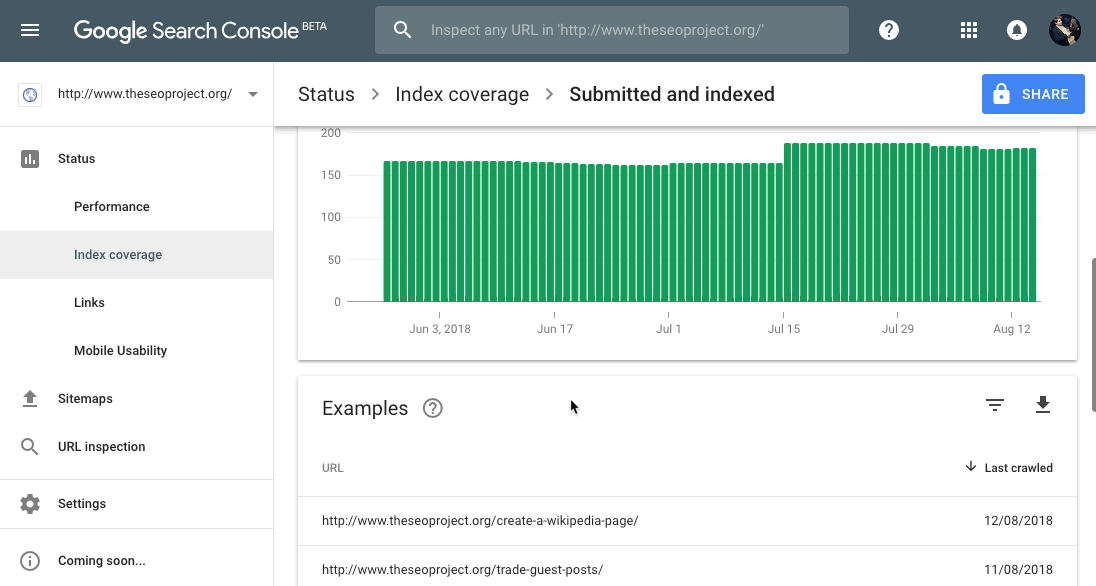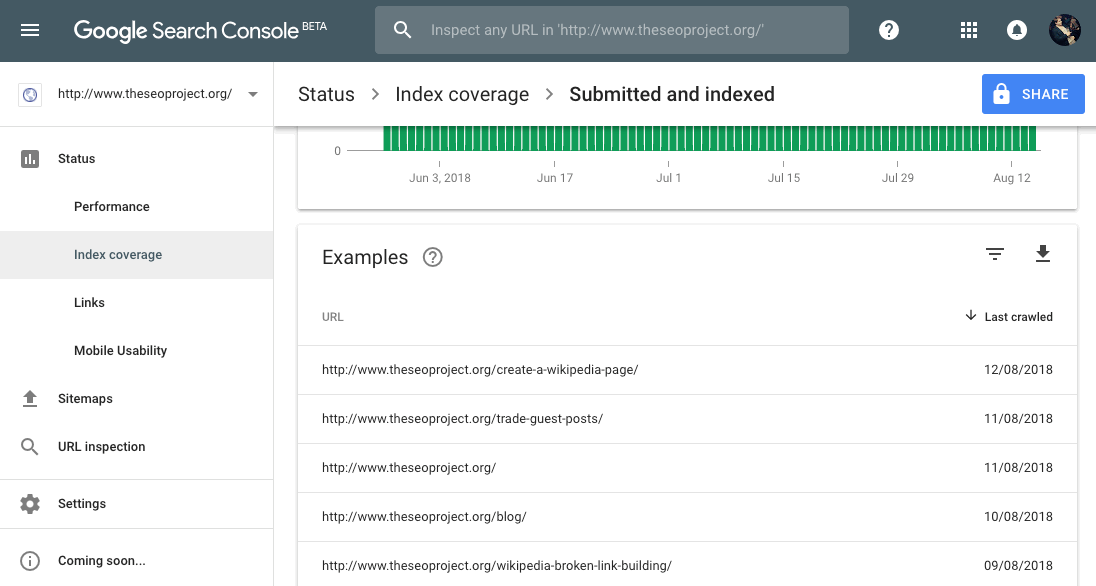
What to do if your website (or webpage) isn’t indexed
If you’ve come to the conclusion that your desired website or webpage isn’t indexed, you first need to figure out why this is.
Here are a few common reasons why this might happen, plus some solutions:
No luck with those? Try Google’s URLinspection tool in the new Search Console.
Search Console > URL inspection > enter page URL > hit enter
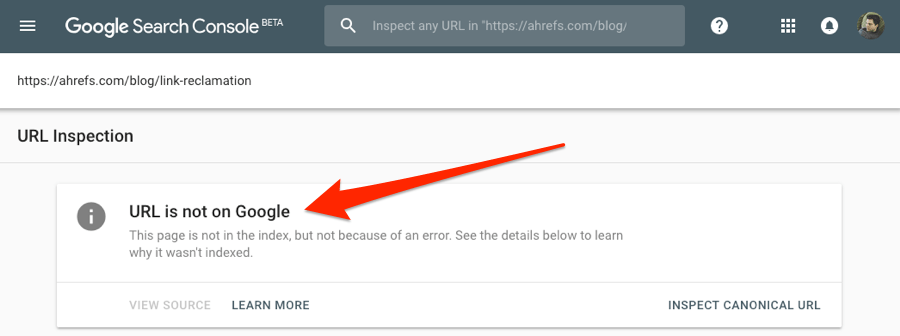
You can see that this URL isn’t indexed in Google. But why?
Scroll down and Google will give more details. With this particular page, it’s because there is a 301 redirect and canonical tag in place.
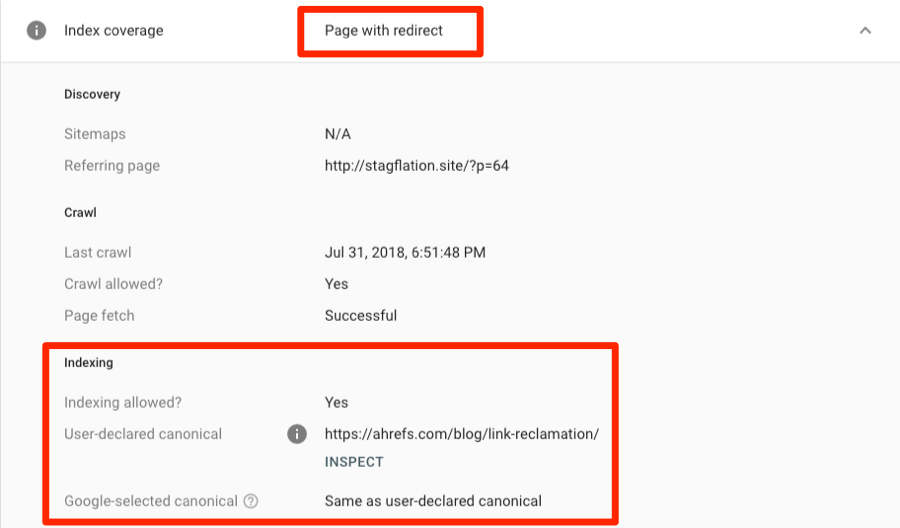
So nothing to worry about in this instance as the canonical URL is indexed. But should Google kick back a genuine error that you aren’t aware of, the next step would be to fix the issue and hopefully, get your page indexed.
Why submitting your website to Google ≠ ranking in Google (and how to fix it)
Most Google searches return thousands, if not millions of results.
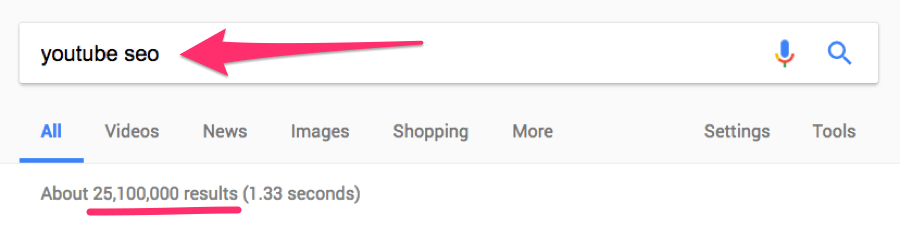
25M+ results for the term “youtube SEO” in Google.
But most people never click beyond the first page, which means that those ranking beyond position #10 receive little to no traffic. For this reason, being indexed doesn’t necessarily mean that people will be able to find your website.
If you want organic traffic, you need to rank on the first page for your target terms (ideally in the top 3 results).
How do you do this? It’s complicated, but one thing you almost certainly need is backlinks.
Google counts links from other websites as votes. So when they’re presented with two or more pages on the same topic, the page with the most links (i.e., votes) will usually rank higher than the pages with fewer links.
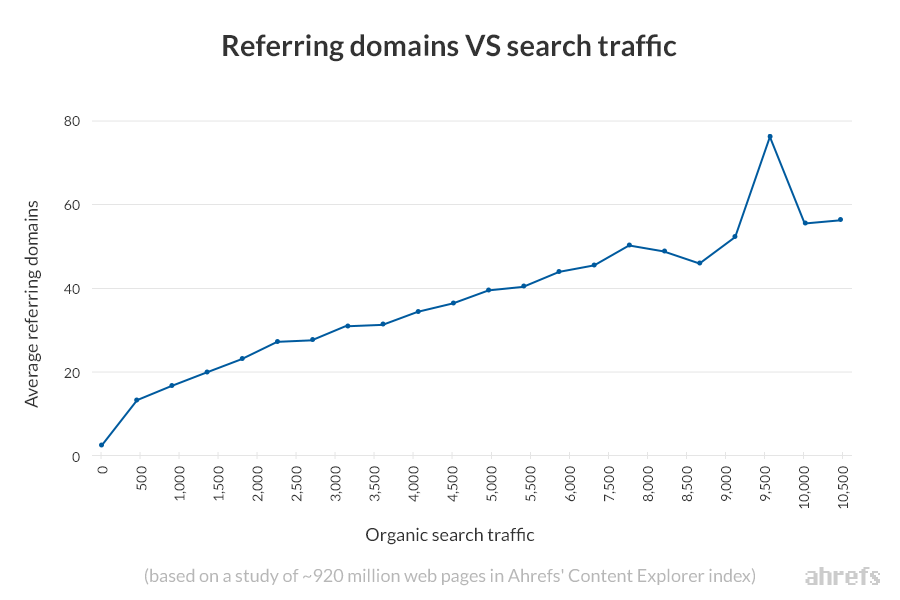
This is not an exact science. We’re absolutely not saying that pages with more backlinks ALWAYS beat those with fewer backlinks. This isn’t true.
Having said that, when we studied almost one billion web pages, we found that the number of referring domains pointing to a web page correlates nicely with the amount of Google search traffic it receives on the whole.

You can use the SERP overview in Ahrefs Keywords Explorer to see how many links each of the current top‐10‐ranking pages have (for your target keyword).
Keywords Explorer > enter the keyword you want to rank for > SERP overview
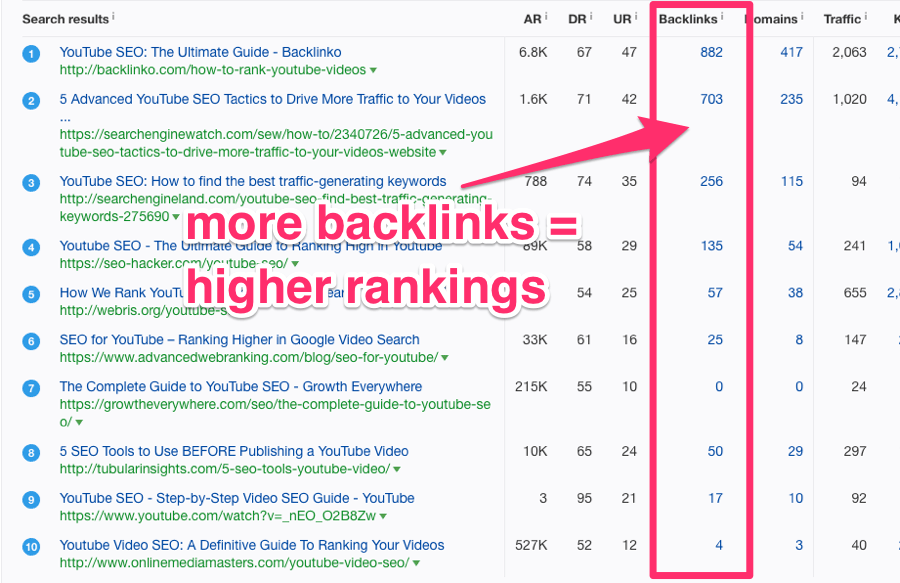
Screenshot taken from Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer. It shows the top 10 ranking pages for the keyphrase “YouTube SEO”.
This will give you a rough idea of how many backlinks you may need in order to compete in the SERP. (You can also look at our Keyword Difficulty score to get an indication of this.)
But it’s not all about links. You also need to make sure your on‐page optimization is up to scratch and that your keyword targeting is on‐point.
Here are some resources to help with each of these things.
Source: www.ahrefs.com








No comments: